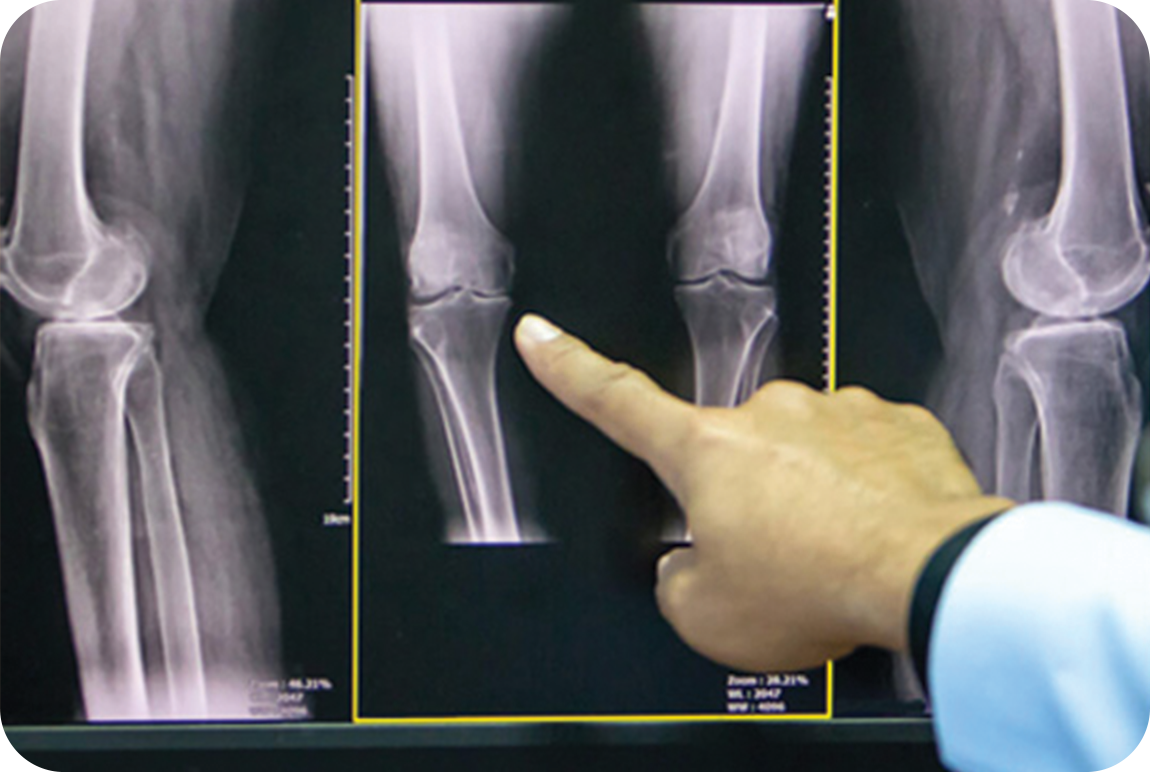
Die Anzeichen und Symptome sind bei den Betroffenen unterschiedlich. Im Allgemeinen weisen die betroffenen Personen Lernschwierigkeiten, spezielle Merkmale im Gesichtsbereich, eine Immunschwäche, Hörschäden und Skelettanomalien auf.1
Zu den charakteristischen Merkmalen im Gesichtsbereich können ein großer Kopf, eine prominente Stirn, ein tiefer Haaransatz, gerundete Augenbrauen, große Ohren, ein abgeflachter Nasenrücken, ein vorstehender Kiefer, weit auseinander stehende Zähne, übermäßig stark ausgebildetes Zahnfleisch und eine große Zunge gehören.2